Dmart (Avenue Supermarts) is one of India’s most successful retail chains, known for its affordable pricing and strong business model. Investors closely follow Dmart’s share price as it reflects the company’s growth, financial strength, and future potential. Dmart Share Price on 24 February 2025 is 3,585.80 INR. This article will provide more details on Dmart Share Price Target 2025, 2026 to 2030.
Dmart Share Price Chart
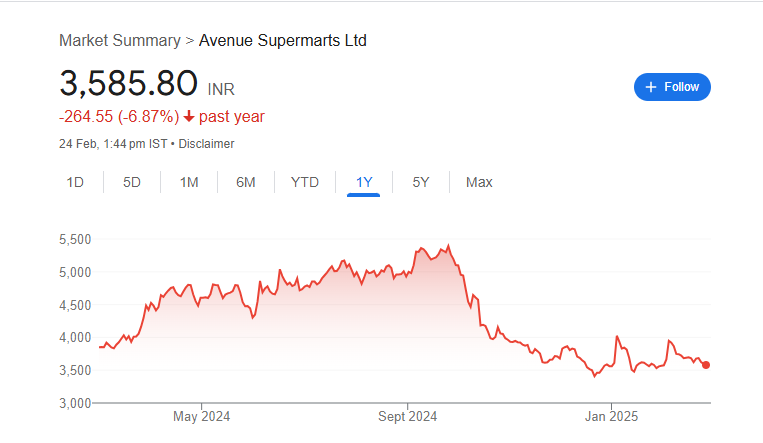
Dmart Share Details
- Open: 3,589.80
- High: 3,611.40
- Low: 3,565.65
- Previous Close: 3,596.70
- Volume: 293,637
- Value (Lacs): 10,531.73
- VWAP: 3,597.37
- UC Limit: 3,956.35
- LC Limit: 3,237.05
- 52 Week High: 5,484.85
- 52 Week Low: 3,399.00
- Mkt Cap (Rs. Cr.): 233,395
- Face Value: 10
Dmart Share Price Target 2025 To 2030
- 2025 – ₹5490
- 2026 – ₹5980
- 2027 – ₹6440
- 2028 – ₹6900
- 2029 – ₹7560
- 2030 – ₹8120
Dmart Shareholding Pattern
- Promoters: 74.65%
- Mutual Funds: 6.77%
- Foreign Institutions: 8.96%
- Domestic Institutions: 1.37%
- Retail and Other: 8.26%
Major Factors Affecting Dmart Share Price
Here are six major factors that can affect Dmart (Avenue Supermarts) share price, explained in a simple and soft tone:
1. Financial Performance
Dmart’s quarterly and yearly financial results play a key role in determining its share price. Investors look at revenue growth, profit margins, and expenses to evaluate the company’s strength. If Dmart reports strong earnings, the stock price may rise, while weak performance can lead to a decline.
2. Consumer Demand & Retail Growth
Dmart operates in the retail sector, where demand depends on consumer spending habits. Higher footfall in stores and increased online sales can boost revenue and investor confidence. However, during periods of low consumer spending, sales may slow down, affecting the share price.
3. Competition in the Retail Market
The retail industry is highly competitive, with companies like Reliance Retail, Big Bazaar, and online platforms like Amazon & Flipkart. If competitors offer lower prices, better discounts, or improved customer experience, Dmart may lose market share. This can impact its stock performance in the long run.
4. Expansion & Store Network Growth
Dmart is known for its strong expansion strategy, opening new stores across different cities. A faster store expansion plan increases growth potential, attracting more investors. However, if the expansion slows down due to high costs or market challenges, it may negatively impact the share price.
5. Raw Material & Operating Costs
Dmart’s business depends on purchasing goods at low prices and selling them at a profit. If costs for raw materials, transportation, or employee wages increase, it could reduce profit margins. Higher expenses without matching revenue growth can put pressure on stock prices.
6. Economic Conditions & Inflation
Macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth directly affect Dmart’s share price. During times of economic slowdown or high inflation, customers tend to spend less, impacting Dmart’s sales. A strong economy, on the other hand, can boost retail growth and positively influence the stock price.
Risks and Challenges for Dmart Share Price
Here are seven risks and challenges that can affect Dmart (Avenue Supermarts) share price, explained in a simple and soft tone:
1. High Competition in the Retail Market
Dmart faces strong competition from Reliance Retail, Big Bazaar, Spencer’s, and online platforms like Amazon & Flipkart. If competitors offer lower prices, better discounts, or faster delivery, Dmart may lose market share. This can impact its revenue and, in turn, its stock price.
2. Economic Slowdowns & Inflation
During economic downturns, people tend to spend less on shopping, which can reduce sales for Dmart. High inflation and rising costs of essential goods may also affect customer spending patterns, leading to lower revenue growth and impacting stock performance.
3. Dependence on Physical Stores
Dmart’s business model is heavily dependent on physical stores, unlike some competitors that have a strong online presence. While Dmart has started focusing on e-commerce, any delay in digital expansion could make it harder to compete with online grocery platforms.
4. Rising Operational Costs
The cost of rent, electricity, employee wages, and logistics continues to rise. If Dmart is unable to control expenses or pass on the extra costs to customers, its profit margins may shrink, affecting its financial performance and stock price.
5. Government Policies & Regulations
Changes in retail sector policies, taxation laws, or foreign investment regulations can impact Dmart’s operations. Any strict government rules or sudden policy shifts may increase costs or slow down expansion, leading to uncertainty in share prices.
6. Supply Chain Disruptions
Dmart relies on a smooth supply chain to keep its stores stocked with essential goods. Events like pandemics, transportation strikes, or global supply chain issues can cause delays in inventory, affecting sales and investor confidence.
7. Slow Expansion in New Markets
While Dmart is expanding, its growth is gradual compared to competitors. Opening new stores requires high investment, careful planning, and local market understanding. If expansion slows down or new stores fail to perform well, it could limit future growth and impact stock performance.
Read Also:- ACE Share Price Target 2025 To 2030- Chart, Market Overview, More Details

